Anatomy of Ear is very important for every Anatomy doctors and students.The human ear has the ability of capturing the sound waves and converting them into electrical pulses. Human hearing can perceive and whisper. The human ear is capable of an adult pick up sounds from 12 to 20,000 Hertz in childhood – up to 22 thousand hertz. It is the organ of hearing and balance at the same time.
The main functions of the ear
- Perceives sound vibrations;
- It provides balance and body position in space
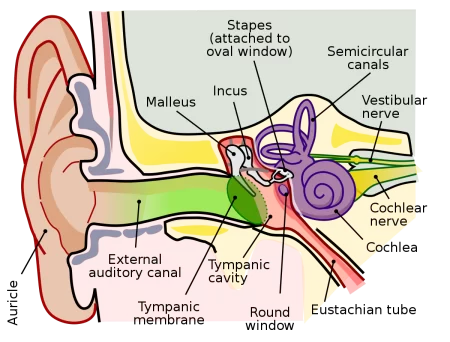
To ensure the reception of sound and responsible to maintain balance its component parts the ear has three parts: the inner ear, outer ear and the middle ear.
The outer ear
The outer ear is responsible for the reception of sound and delivering them to the eardrum. Outer ear consists of the pinna (which is a cartilage tissue with swirls) and the ear canal, which starts from the middle ear and emits large amounts of earwax necessary to protect the ear canal from dirt and dust.Pinna has a complicated configuration and a cartilage plate coated on both sides of the skin. It is based on the exception of the area of the lobe.
Elastic cartilage is covered with skin and perichondrium. The auricle is attached by ligaments and muscles from the top to the scales of the temporal bone, behind – mastoid. It is a funnel that ensures optimal perception of sounds at a certain position of power. The external auditory meatus has a length of 2.5 cm, and the elastic ends of the tympanic membrane that separates the external ear from the middle.
The rear wall of the auditory canal is a front wall of the mastoid.
Middle ear
The middle ear tympanum represented about 1 cubic centimeter, which placed three ossicles: hammer, anvil and stirrup. The Vibrations of the eardrum are transmitted hammers.The cavity of the middle ear using the hearing or eustachian, pipe communicates with the nasopharynx. By hearing the tube into the tympanic cavity air enters, so that the pressure on the eardrum from the tympanic cavity aligned. If the difference in pressure on either side of the membrane is large, membrane may rupture.
In the inner wall of the tympanum, which separates the middle ear from the inside, there are two holes – round and oval, covered by a membrane.
The main function of the middle ear – conducting sound from the eardrum through the auditory ossicles to the oval window that leads to the vestibule.
You Must Understand The Ultimate Guide of Anatomy of The Ear
The tympanum – slit space volume of 0.75 cm3, located in the pyramid of the temporal bone; it communicates with a cave, in front – through the Eustachian tube to the nasopharynx.The tympanic cavity walls are six: top, bottom, front, back, inner (medial), outdoor.
The outer wall of the tympanic cavity consists of the tympanic membrane, which separates only the middle part of the cavity.
The tympanic membrane consists of three layers:
- Outdoor – epidermis
- Internal – mucosa
- Middle – fibrous.
In the tympanum, there are three divisions:
- Top – nadbarabannoe space – epitimpanum
- Average – the largest in size – mezotimpanum
- Lower – gipotimpanum
The tympanum contains three ossicles: hammer, anvil and stirrup, which are connected by joints to form a continuous chain, located between the eardrum and the oval window.
Eustachian (auditory) tube is covered with a mucous membrane; its length is usually about 3.5 cm. It distinguish bone portion located at the mouth of the drum about 1 cm long and membranous-cartilaginous nosoglotnogo at the mouth of a length of 2.5 cm.
Mastoid:
The tympanum is connected via a relatively wide passage to the antrum, is a central pneumatic mastoid cavity. In addition to the mastoid antrum is normal, there are several groups of cells disposed throughout its thickness, but they are communicating by means of narrow slits antrum, either directly or through other cells. Between the cells are separated by thin bony partitions having holes.
The inner ear
The inner ear is located in the temporal bone and membranous labyrinth. The membranous labyrinth is located inside the bone, between them there is a space filled with perlymph. Inside the membranous labyrinth has a fluid called endlymph. In the inner ear have a cavity formed by a spiral, which is called the cochlea. From the middle ear, it demarcated oval hole. Snail includes basic and vestibular membrane. Each of them is divided into three sections filled with fluid.
The chain of small bones:
The auricle collects sound waves are reflected in the folds, passing into the ear hole, and eventually strike the eardrum. The tympanic membrane vibrates with a specific frequency and height.
A chain of small bones of the middle ear increases the oscillatory motion and begins to transmit its oval hole in the inner ear. Mechanical energy from sound waves into electrical energy transferred due to the fact that the fibers of the auditory nerve excite spiral organ, located in the cochlea and the auditory sensation is transmitted to the brain.
How is the perception of sound?
Sound vibrations, are captured by the pinna, extend further into the auditory canal, and then fall on the eardrum, which catches them and produces vibration. They enter through the auditory ossicles in the second ear foramen ovale (windows), which leads into the cavity of the inner ear.
The fluctuations of the membrane affect the spiral snail. All fluctuations in the confined space occur due to the membrane of the round holes (windows). Passing perilymph, sound waves hit the endolymph, which in turn causes anxiety fibrils basilar membrane.
They are cells in the organ of Corti. And these cells are transformed with the sound waves, creating a process of nervous excitement. He auditory nerve is projected in the temporal cortex, is processed there as information which sound is currently hearing a person.
Transplantation of ear
The person who lost the ear, for example, in a car accident has a chance to rediscover a new, identical body. Currently, this is done through the cultivation ears. For the first time raised the ear in the laboratories of America. To grow new body took the mouse to the back of which were administered ear cartilage cells. The organism has successfully received the implant grown in this manner.
At present, hundreds of such operations performed in the United States. A cheaper option, replacing the ear is prosthetic. The prosthesis is an artificial ear is made of hypoallergenic silicone. Such operations are restoring normal way a person’s face after emergencies are performed worldwide. For babies with a complete lack of ears physicians and biomedical scientists from Cornell created ears using the injectable matrices and 3- D printing