Theories of management are very important for any business and organization. The experts have presented different management theories for the successful running of organization. These ideas are called as six theories of management.Here is the list of Different types of management theories are discussed in details.
Scientific Management theory
This theory was presented by Frederick F Taylor.He gave the idea to run the organization in scientific way. The principles of this theory are:
- All work should be done in limited time. The work done should be measured accurately. This aims at how a piece of work could be done efficiently.
- Management should take the responsibility for planning the work. Workers should be made to execute the task.
- Management should scientifically determine the best methods and should train the workers accordingly. Management should be trained and should be taught to apply scientific principles of management and control e.g. in selection and training of workers.
- Wages should be according to output.
- This theory aimed at lowering the unit cost by increasing the efficiency of management It is rigid and focused on discipline, high concentration on job and strict incentive pay system.
Administrative Management Theory
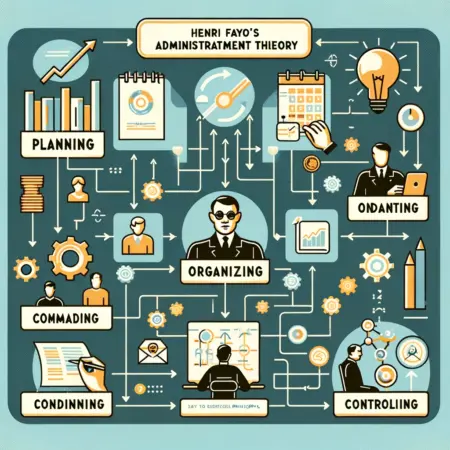
This theory was presented by Henri Fayol. He focused his attention on manager rather than worker. He emphasized the training of the managers for improving die organization. He defined administration in terms of five functions which are:
- Planning
- Organizing
- Commanding
- Coordinating
- Controlling
Fayol’s 14 Principles of Management

- Division of Labor
The more people specialize, the more efficiently they can perform their work. The principle is epitomized by the modern assembly line.
- Authority
Managers must give orders so that they can get things done. While their formal authority gives them the right to command, managers will not always compel obedience unless they have personal authority (such as relevant expertise) as well.
- Discipline
Members in an organization need to respect the rules and agreements that govern organization. Discipline will result from good leadership at all levels of the organization, fair agreements (such as provision for rewarding superior” performance), and judiciously enforced penalties for infractions.
- Unity of Command
Each employee must receive instructions about a particular operation from only one person. When an
employee reported to more than one superior, conflicts in instructions and confusion of authority would result.
- Unity of Direction
Those operations within the organization that have the same objective should be directed by only one manager using one plan. For example, the personnel department in a company should not have two directors, each with a different hiring policy.
- Subordination of Individual to the Common Good
The interests of employee should not take precedence over the interests of the organization as a whole.
- Remuneration
Compensation for work done should be fair to both employee and employers.
- Centralization
Managers should retain final responsibility but also need to give their subordinates enough authority to do their jobs properly. The problem is to find the best amount of centralization in each case.
- The Hierarchy
The line of authority in an organization often represented today by. the neat boxes and lines of the
organization chart-runs in order of rank from top managers to the lowest level of the enterprise.
- Order
Materials and people should be in the right place at the right time. People in particular should be in the jobs or positions most suited for them.
- Equity
Managers should be both friendly and fair to their subordinates.
- Stability of Staff
A high employee turnover rate is not good for the efficient functioning of an organization.
- Initiative
Subordinates should be given the freedom to conceive and carry out their plans, even though some mistakes may result.
- Esprit de Crops
Promoting team spirit will give the organization a sense of unity. Even small factors may help to develop this spirit. Fayol suggested the use of verbal communication instead of formal, written communication whenever possible.
The Ultimate Guide To Theories of Management And The Management Leadership Theories.

- Behavioral Management Theory
This theory was put forward by Elton Mayo. He was of the view that production depends on the way people are treated. He. focused on five concepts as under:
- Morale
- Group dynamics
- Democratic supervision
- Personal relations
- Behavioral concept of Motivation
Bureaucratic Management Theory
This theory was advocated by Max Weber. He focused on the structure of organization. He considered that highest degree of efficiency can be attained through this approach. By using this approach it is possible to take control over human beings. Its characteristics are:
- There is the rigidity of official behavior
- There is resistance to the adoption of innovations and change
- There is rigidity of rules and regulations
- The decision is taken by a hierarchy of officers and officials; .;
- There is the leveling of talent. This system tends to reduce the performance of bright workers to the level of mediocrity
- The consequence is the ‘red tape which is never in the straight line. All feel entrapped and helpless.
Theory of Management by McGregor
Its basic assumptions are given below:
- The average human being has an inherent dislike of work
- The average human being avoids work if he can
- Because of the human characteristics of dislike of work, there arises the need for control and direction of individuals. The individuals are threatened with punishment to get them to put forth adequate effort for the achievement of objectives of an organization.
- The average human being wants security
‘Y’ Theory of Management by Douglas
- The average human being does not inherently dislike work
- Self-control and self-direction are perhaps more powerful means than external control and the threat of punishment for bringing about better results.
- Self-actualization is the highest level need of the worker
- The average human being works under proper conditions not only to accept but also to seek responsibility •
- The capacity to exercise a relatively high degree of imagination and creativity in the solution of organizational problems is wisely distributed in the management personnel parts.
Activity of one part affects the activity of the other part. Terms such as cooperation and interaction of separate departments, open and closed systems, system boundary and feedback were used.
According to this approach no single idea/ concept can yield the one best way of administration. Different ideas or concepts help in different situations. The best is one that is according to situation. So find out the “best” depends upon the wisdom of the manager.
Contingency Approach of Management
According to this approach no single idea/ concept can yield the one best way of administration. Different ideas or concepts help in different situations. The best is one that is according to situation. So find out the “best” depends upon the wisdom of the manager.
The Significance of Management Theories
Why are management theories so important in modern organizations? Let’s explore their significance:
- Guiding Principles: Management theories provide a set of guiding principles that managers can follow to make informed decisions and navigate complex organizational dynamics. They offer frameworks for effective planning, organizing, leading, and controlling functions.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By applying management theories, organizations can streamline their processes, improve productivity, and optimize resource allocation. Theories such as scientific management focus on eliminating inefficiencies and maximizing output.
- Effective Leadership: Management theories shed light on different leadership styles and their impact on employee motivation and performance. By understanding these theories, managers can adapt their leadership approach to inspire and engage their teams effectively.
- Organizational Development: Management theories play a crucial role in supporting organizational development and change management initiatives. They provide insights into managing resistance to change, fostering innovation, and sustaining competitive advantage.
- HR Practices: Understanding management theories helps HR professionals design effective recruitment, training, and performance management strategies. These theories guide the development of employee-focused policies and programs that drive organizational success.
- Decision-Making: Management theories offer a systematic and structured approach to decision-making. By considering the principles and concepts from various theories, managers can make informed choices that align with the organization’s goals and values.
Conclusion.
In conclusion, theories of management provide valuable insights and frameworks for effective managerial practices. From scientific management to contingency theory, each theory offers unique perspectives on managing people and resources in organizations. By understanding and applying these theories, managers can enhance organizational performance, foster employee satisfaction, and drive sustainable success.
