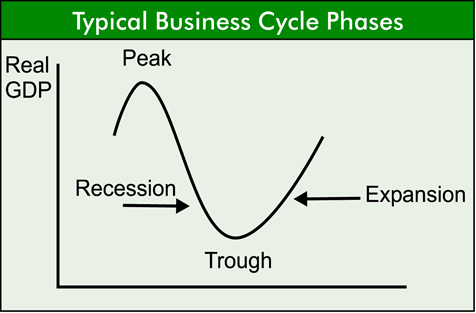
Phases Of Trade Cycle is composed of four following phases. It is very important for Business student. The trade cycle, often referred to as the business cycle or economic cycle, represents the fluctuations in economic activity over time. These fluctuations are characterized by periods of growth and contraction. The trade cycle typically consists of the following four phases:
You Must Know The Phases Of Trade Cycle In Economics In Order to Control Inflation.
1- Depression
Depression is such a harsh economic situation in which the level of economic activity, national income, employment and output falls to lowest level.
Main Features
- Value of money is very high but that of man is very low. Money can purchase greater quantity of goods and services but the man can purchase nothing as he is not getting employment.
- Prices are falling at a faster rate than the cost of production, therefore profits convert into losses.
- No doubt the rate of interest is low but expected profit is much lower than the prevailing rate of interest which makes investment unprofitable.
- Decrease in investment leads to many times more decrease in income and employment through the negative effect of multiplier.
- Quality of life is very low and the people are hardly meeting the mere necessities of life.
- Pessimism prevails everywhere.
- The lowest point of depression is known as “trough” where income, employment and output is at the lowest possible level
2- Recovery or Revival:-
Business cannot remain in depressed form forever. Actually the lowest point of depression contains the germs of recovery in itself. At the lowest point of depression, aggregate demand exceeds the aggregate supply of goods and services. Excess of demand over supply raises the general price level. Profit margins reappear because cost of production fall below the general price Level. It provides incentive for the entrepreneur to invest their resources in productive activities. Many factors develop which start the up-turn in the economy.
Main Features
- General Price level starts rising and profit margins are reappearing.
- Expected rate of profit becomes higher than the rate of interest which provides incentive for investment.
- Workers employed by one industry create the demand for the goods produced by so
- Many other industries.
- Revival of investment in one industry causes the revival of Investment in so many other industries.
- Pessimism is converted into optimism.
3- Expansion or Prosperity or Boom
After some time the phase of revival enters the phase of expansion. In this phase the level of economic activity, national income output and employment is expanding very rapidly. Since aggregate demand is increasing, therefore, the producers are confident about the sale of output. The wave of optimism induces the entrepreneurs to make investment in many sectors of the economy. Increase in investment expands national income and employment through the combined effect of multiplier and accelerator. After sometime, the economy achieves an ideal situation i.e. full employment and after that real inflation starts in the economy. The highest point of expansion is known as boom.
Main Features
- Demand for consumption and investment of goods is expanding rapidly.
- Prices are rising at a faster rate than the cost of production.
- Expected rate of profit is greater than the prevailing rate of interest therefore investment becomes more attractive than lending.
- Volume of credit is expanding.
- Optimism prevails everywhere.
4- Recession or Contraction:-
Just as the lowest point of depression contains the symptoms of recovery in itself, the boom of expansion contains the germs of recession. The expansion phase of trade cycle distributes national income in favor of profit earning class. A small group of people receives foremost portion of national income and majority of population gets a small portion of income. Unfair distribution of income decreases aggregate demand and over production occurs in the economy. Over production decreases the general price level and profits are covered into losses. It causes down-turn in the economy.
Main Features
- Total supply of goods and services cannot be sold due to insufficiency of aggregate demand.
- Aggregate demand is insufficient due to unfair distribution of national income.’
- Insufficient demand causes a decrease in the general price level.
- At the boom of expansion, competition is so perfect that profits are just normal.
- Fall in prices converts profits into losses.
- Entrepreneurs decrease their production and the level of employment starts contracting.