Mucormycosis is an acute and usually fulminant systemic fungal disease originating in the paranasal sinuses, orbit, bronchi, or intestines and disseminating by the hematogenous route to the brain, kidney, heart, and other organs.
History of Mucormycosis.
In 1876 Furbringer reported the firs: doeaaaeaAei case of human pulmonary mucormycosis. In 1854 demonstrated the pathogenicity of Mucorales in rabbits.. aaut in 1885 Paltauf first described a case with central nerves ‘Weani involvement. Baker, Bauer, and Sheldon have made iaw SaBinuS recent contributions to our knowledge of the pathogenesis of the disease.
Etiology of Mucormycosis.
Mucormycosis is caused by species of three genera—Absidia, Rhizopus and Mucor—of the order Mucorales. In tissues fungi appear as broad (6 to 50 fx), nonseptate hyphae. On Sabouraud glucose medium at room temperature there is rapid growth of a large, aerial mycelium that microscopically consists of hyphae bearing large (100 /a) globular sacs (sporangia) containing small (6 to 8.5 n.) round to elliptical bodies (spores). Laboratory animals, especially those treated with steroids or made diabetic by alloxan, can be experimentally infected.
Epidemiology of Mucormycosis.
The disease is worldwide in distribution. It occurs equally in all races and at all ages, but twice as often in males. A prominent feature of illness is the association with diabetes mellitus (40 per cent of cases) and less frequently with leukemia, lymphomas, tuberculosis and burns. Fungi of the order Mucorales readily colonize dead plant and animal tissues and are exceptionally widespread saprophytes in soil and fruits. They are commonly called “bread molds.” Infection is exogenous. In experimental infections in laboratory animals, induction of diabetic acidosis by alloxan has been shown to impair tissue mast cells and the degranulation and migration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to the site of infection. Naturally occurring disease has been reported in horses, dogs, cows, pigs, and birds. Animal-to-man or man-to-man spread is not: known to occur.
Pathology of Mucormycosis.
The histopathology of mucormycosis is characterized by necrosis, acute mfam~ mation, and suppuration. An especially prominent feature is early invasion of blood vess date with arteritis, thrombosis, and infarction. Giant cells are seen occasionally. Lesions may be found in the central nervous system, orbit, paranasal sinuses, lung, gastrointestinal tract, skin, heart, and kidneys.
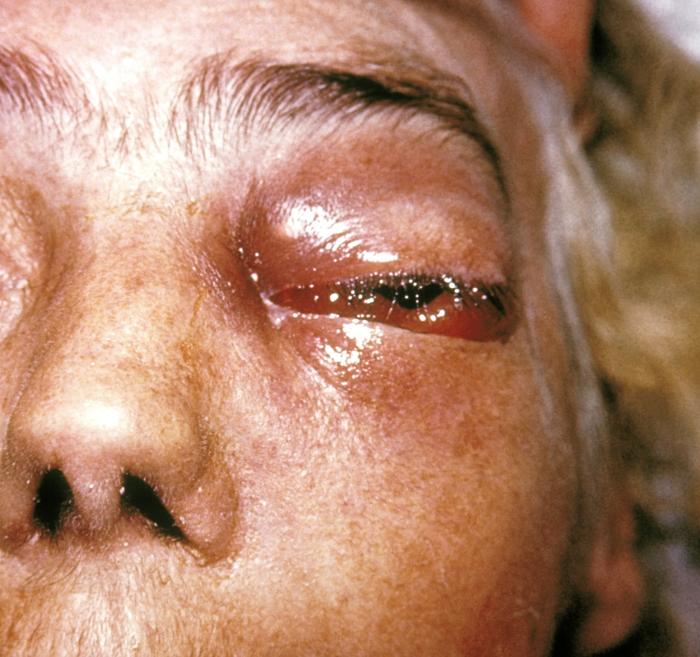
Clinical Forms of Mucormycosis.
Mucormycosis is an acute, inflammatory process either in the nose or paranasal sinuses with purulent nasal discharge and a characteristic gangrenous nasal mucosa, or unilaterally in the orbit with ophthalmoplegia, edema, proptosis, and chemosis. Disease may then spread to involve heart, kidneys, or brain (one third of cases).
Lung disease is that of a primary pneumonia followed by infarction and abscess formation. Myocardial infarction from mycotic occlusion of a coronary artery has been reported in three patients. In the gastrointestinal form ulcerations are produced, usually in the terminal ileum and large intestine or rarely in the esophagus and stomach. There is a preponderance of cerebral involvement in diabetic patients, of the pulmonary form in leukemic patients, and of more widespread disease in nonleukemic, nondiabetic patients.
Diagnosis of Mucormycosis.
Although the large nonseptate hyphae are distinctive when seen in stained tissues, the diagnosis is confirmed and the genus of Mucorales identified only when the fungus is isolated in culture.Mucormycosis must be distinguished from acute cellulitis and central nervous system infection owing to pyogenic bacteria, from tuberculosis or other fungal disease of the lung, and from ulcerative enteritis and colitis of other causes.
Treatment of Mucormycosis.
Amphotericin B (see Histoplasmosis) is effective in experimental infection in the rat, has been used in a few patients, and deserves additional trial. The amount of drug necessary has not been determined.A few patients have responded to control of the underlying diabetes and one at least to surgical resection of diseased tissue.
Mucormycosis Prognosis.
Until 1955 the patients in all cases reported had died. Recently a few patients have responded to control of the underlying diabetes, to resection of diseased tissue, and to amphotericin B treatment. The disease should be considered potentially and rather rapidly fatal if untreated.