The cyclotron was created by Ernest Lawrence , with the help of his guardian, Stanley Livingston , in 1929-1930.It was developed for producing a stream of electrically charged atoms or nuclei travelling at a very high speed. It consists of an evacuated enclosure lying between the flat, circular pole pieces of a large electromagnet
The cyclotron was created by Ernest Lawrence , with the help of his guardian, Stanley Livingston , in 1929-1930.It was developed for producing a stream of electrically charged atoms or nuclei travelling at a very high speed. It consists of an evacuated enclosure lying between the flat, circular pole pieces of a large electromagnet
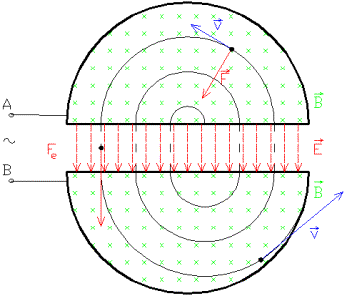
Within this enclosure are two ‘dees’, rather like the two halves of a flat closed tin of polish which has been divided along a diameter, i.e. shaped like the letter D. An alternating electric field is set up between the dees, and charged atoms are released between them.
The electric field accelerates each ion to a high speed, and after the ion has passed out of the region between the plates it enters the dee itself where there is no electric field but where the magnetic field causes it to travel in a circular path about the axis of the pole pieces of the magnet. After it has traversed a semi-circle the atom is again in the space between the plates, and if the electric field is now reversed the atom is not retarded, but is further accelerated.
It now traverses another semicircle of larger radius because of its increased speed, returning to the space between the plates at a time when the electric field has again been reversed, and The time to traverse one half-circle depends only on the nature of the particle and the (fixed) magnetic field. In this way the speed of a stream of charged atoms is gradually built up until their velocity is enor-mous, and they are travelling near the edge of the circular enclosure. The stream is allowed or caused to pass out at one point near the edge, and to fall on a target of a suitable material. The cyclotron can be used to produce protons with energies up to about 10 for pole piece diameters of about 60 ins., without undue difficulty.
Near this energy, the relativistic increase of mass of the accelerated particle becomes significant and the faster particles get out of step with the slower particles. The time to traverse one half-circle is wmf He, where m is the mass and e the charge of the particle, and H the magnetic field, and clearly depends on tn. Machines have been designed to overcome this difficulty using magnetic fields that vary together with the frequency of the electric fields.
Frequency of A Cyclotron
It is very simple to show that the period of the circular motion of a charge within a magnetic field does not depend on the radius of the trajectory. For this, the following steps are followed.
- -The speed of the particle can be expressed as a function of the period T of its circular motion
by the expression v = 2pr / T
- – We can deduce another expression of v taking into account that the magnetic force acting on the load F = qvB is the centripetal force F = mv2 / r of the circular movement that it describes. It is obtained that v = rqB / m
- – Equaling both expressions of velocity can clear the period T = 2 pm/qB.
Dependence does not appear with the radio.This result is important as it constitutes the basis of operation of cyclotrons.
Cyclotron Functionality
The cyclotron uses a constant magnetic field and an electric field of constant frequency to accelerate particles. As the particles – in this case, the protons – are accelerated, they move in a spiral path. Each time the particles complete one turn, their velocity increases, approaching even the speed of light. A cyclotron is capable of accelerating until it reaches high energy, without requiring high voltages.