Chromosomal theory of inheritance . Better known as Sutton and Boveri chromosomal theory , it states that Mendelian alleles are located on chromosomes . This theory was independently developed in 1902 by Theodor Boveri and Walter Sutton . It remained in controversy until 1915 , when Thomas Hunt Morgan got it accepted by the world.
The chromosome theory of inheritance, according to which chromosomes are the seat of genes , is based on the following assumptions:
- the close analogy between the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis and that of genes, foreseen by Mendel’s laws;
- the presence of chromosomes in gametes;
- the presence of a maternal and a paternal chromosome in somatic cells.
The traits of a new individual are determined by specific genes present chromosomes inherited from the father and mother. The human are approximately 100,000 genes in the 46 chromosomes.
Genes that are located on the same chromosome tend to be inherited together and for this reason it is known as linked genes. In somatic cells , chromosomes are presented as 23 homologous pairs to form the diploid number of 46. There are 22 pairs of paired chromosomes, autosomes and a pair of sex chromosomes.
If the pair of sex chromosomes is xx the individual is genetically female, if the pair is xy , the individual is genetically male.
One chromosome of each pair comes from the maternal gamete , the oocyte , and the other component of the pair comes from the paternal gamete, the sperm . Thus, each gamete contains a haploid number of 23 chromosomes and the union of gametes in fertilization restores the diploid number of 46.
The main provisions of the chromosome theory of heredity of Morgan were formulated :
- genes responsible for the inheritance of traits are located on the chromosomes;
- genes are located linearly, each gene has its own place in the chromosome – the locus;
- the set of genes on each chromosome is unique;
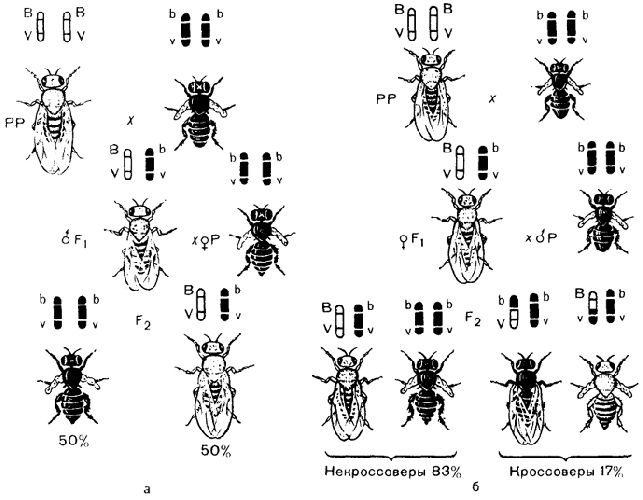
- groups of genes located close to each other are inherited linked;
- the number of linked genes is equal to the haploid set of chromosomes and is constant for each species (a person has 23 pairs of chromosomes, therefore, 23 pairs of linked genes);
- cohesion of chromosomes is broken during crossing over (crossover) – the process of exchanging chromosome sites in prophase I of meiosis;
- the farther away from each other are linked groups of genes on the chromosome, the greater the likelihood of crossing over.