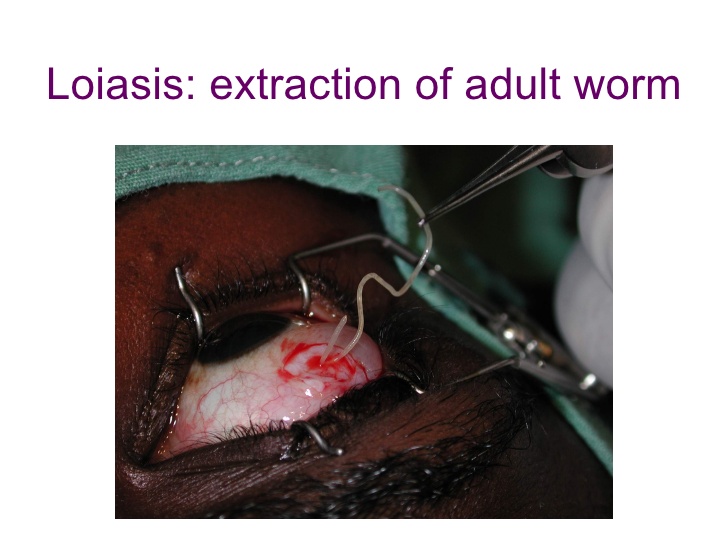
Loiasis or Loa loa infection is characterized by the appearance of transient swellings mainly on the limbs; these are thought to be the site of the migrating adult worms in the subcutaneous tissue. Occasionally a worm will traverse the conjunctiva of the eye.
The male adult worm is 30 mm. long and the female 70 mm. ‘They live for many years, and gain access to the body through the proboscis of biting flies (deer flies of the genus Chrysops). These worms appear to be in a state of continuous migration in the subcutaneous tissues of the body. It is not clearly understood how the sexes locate each other, but they meet and mate, and the female produces microfilariae that appear in the blood during the day and are infective to the insect vector. .
Man is the only reservoir host, with the possible exception of monkeys. Human loiasis is restricted to Africa, mainly the West Coast. It occurs from Sierra Leone to the Cameroons and extends into the heart of Africa in the region of the Congo basin.
Clinical Manifestations of Loiasis.
The main clinical manifestation is the repeated occurrence of hot erythematous swellings (5 to 10 cm. or more) called Calabar swellings after the endemic area of Calabar. These occur in the upper limbs particularly, are painful, and subside in a few days. They are associated with the presence of an adult worm. A similar swelling occurs around the eye when the adult worm crosses the eye beneath the conjunc-tivae. The patient notices the worm in his line of vision (“like a submarine, doctor”) and it is worth inquiring for such a history. Calabar swellings seem to occur more frequently in the extremities. Why this is so is not known. Routine roentgenography in endemic areas often reveals calcified dead worms lying between the metacarpals. Rarely, neurologic symptoms may be associated with the infection if the Calabar swelling involves a peripheral nerve. Also the parasite has been found in the cerebrospinal fluid associated with a meningoencephalitis.
Diagnosis of Loiasis.
The initial diagnosis is usually based on a history of Calabar swellings in a patient coming from an endemic area. Examination of the daytime blood reveals sheathed microfilariae with «a characteristic distribution of caudal nuclei. In early loiasis, microfilariae may not be detected even by concentration techniques. Very high eosinophil counts are encountered at this stage (50 to 70 per cent). A positive filarial complement-fixa-tion test is usually present. Occasionally the adult worm can be extracted as it crosses the eye. It has been suggested that another human filarid, Acanthocheilonema perstans, may cause Calabar swellings.
Loiasis Treatment.
Diethylcarbamazine (Hetrazan) kills both adults and microfilariae. One course of 12 mg. per kilogram of body weight for 14 days is all that is necessary. Reactions are rare.