Intravenous injection when given for small quantity (1 cc to 50 cc) it is given through vein directly, through syringes. When larger quantity is required to be injected like glucose or normal saline it is called intravenous infusion.
- When very quick action is required like cardiac stimulants, respiratory stimulants, anti-spasmodics, methergine etc
- When the drug on giving intra muscularly or hypodermically would cause local irritation.
- When large quantity of drug required to be given—serum, saline or glucose.
- For diagnostic purpose—IVP etc. ‘
- In treatment of varicose veins.
- In case of loss of fluid in body such as haemorrhage, boro, surgery.
- For general anaesthesia purpose.
- To maintain acid and base balance.
Site of Injection
Large superficial veins are selected for purpose of mtra-venous route. Usually site is large vein at cubital fossa, the next site is visible superficial vein at dorsum of palm or hand. When due to severe dehydration in burn or haemorrhage these sites are not available or poses problem, femoral vein over front of thigh is tapped for Intravenous purpose. Only expert hand can do such tapping. Some times veins at inner side of ankle is also selected. When needle punctures these veins and it becomes difficult them intravenous route is adopted by cutting the skin & finding a vein either at dorsum of hand or above medial malleolus at ankle joint. This method is known as venesection.
Procedure for IntraVenous Route
- Sterile syringe and needle of the size required according to quantity of drug is kept ready
- A rubber tourniquet or blood pressure cuff is tied on the upper arm to cause accumulation of blood and engagement of veins.
- The skin at the site of injection is cleaned with spirit swab.
- The hand of patient is made steady by holding it with your left hand.
- The needle is inserted at above an angle of 30° to the skin surface.
- When the needle pierces the vein, blood comes out in syringe and then push the piston of syringe to inject the drug slowly.
- When the needle is removed, the vein is pressed with the sponge and the forearm is flexed so as to collapse the vein and prevent bleeding.
Intravenous infusion or drip
Material Required
1. Sterile infusion set either disposable or rubber boiled set. 2. No. 19 or No. 20 sterile needle. 3. No. 18 air vent needle. 4. Murphy drip bulb. 5. Rubber tube and screw lamp. Drug or sol to be injected. 7. Tourniquet. 8. Spirit swab. Adhesive tape. 10. Bandage and Scissor. 11. Arm board, mackintosh, bandage. 12. I.V. Infusion stand
Procedure
- Intimate the patient about the procedure.
- Wash your hand with soap and water.
- Keep adhesive plaster of 8 cm length two or three pieces attached to infusion stand.
- Hang the infusion bottle in stand. Insert the infusion set needle in bottle.
- Insert air-vent needle to the rubber stopper of bottle and watch that fluid runs into the infusion rubber tubing up to the needle to make it air-free.
- Now close the screw clamp to-stop further flow of fluid.Clean the skin over vein and when blood flows in, release the tourniquet
- Tic tourniquet over upper arm and ask the patient to open and close fingers.
- Correct splinting of Leg for I.V. Note that any straying must be taken over bony prominence to prevent constriction of blood vessels.
- Correct splinting of arm for I.V. note to prevent wrist drop.
- A space is left between bandage to frequently see if any swelling. The tube is fixed at extra length of splint to reduce movements.
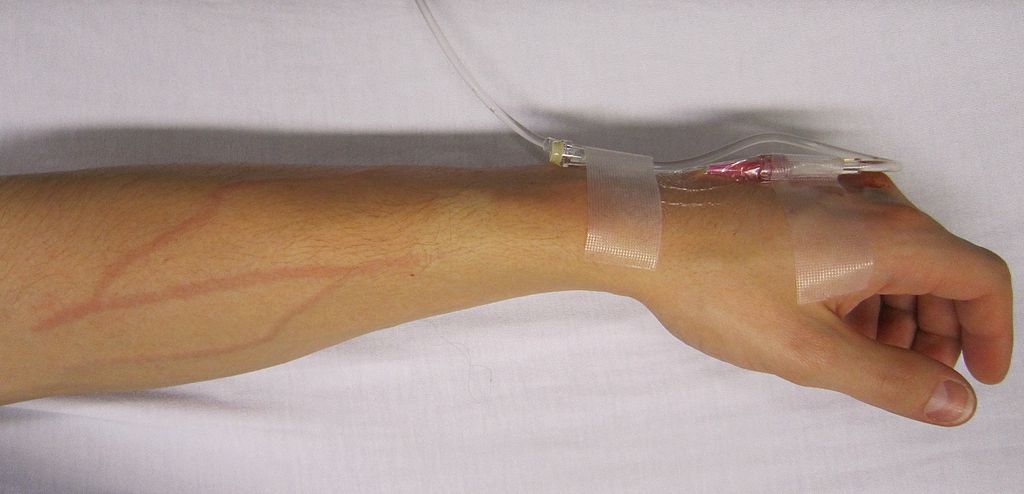
- Apply adhesive plaster over base of needle to fix to the skin-
- Regulate the flow of fluid upto desired drug per minute.
- Keep the hand on the arm board fixed with bandage.
- In extreme cold weather tie a hot water bottle on infusion bottle to keep it warm.
Points to Remember in I. V. Infusion
- Maintain steady rate of flow of fluid. The thicker the fluid the lesser the rate.
- Instruction from attending doctor should be obtained regarding increasing or decreasing the rate of flow.
- Advise the patient or attendant to Keep the hand in proper position and to watch for any swelling at the site of needle.
- Observe the bottle frequently specially when it is nearing to neek during finishing time.
- Record the I.V. drip in chart.
- Clamp the fluid while changing for a second bottle.
Remedies for Stoppage of Flow
- Open the clamp or further loosen it.
- Turn the rubber air vent around.
- Observe if the rubber tube is kinked or twisted.
- Elevate the limb or change the position of the needle by placing a cotton swab under it.
- Massage near about the site of needle.
- See if the patient has changed the position of hand bending or putting pressure of head over hand.
- Raise the height of bottle on stand.
- To release blockage of needle, take a little solution from I.V. bottle and push it through I.V. needle.