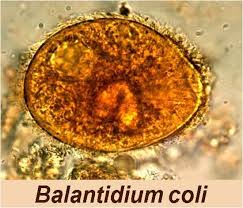
Balantidium coli is the largest protozoon of man, measuring 50 to 70 /z in length by 30 to 60 in width. It infects the colon of man and may produce diarrhea and dysentery. When viewed under the low power of the microscope in a saline smear of stool, the grayish-green trophozoite can be seen gliding across the field powered by spiral longitudinal rows of cilia. There is a large oral macronucleus and a smaller micronucleus. A cytostome or mouth ingests organic matter that circulates as food vacuoles.
Erythrophagocytosis has been observed. Reproduction is by binary fission or conjugation. A resistant cyst form is passed in formed stools, and this is the infective form. Cosmopolitan in distribution, it is a rare infection of man although common in pigs. When man and pig share shelter, human infections are common, and this accounts for the high incidence of human infection in parts of New Guinea (20 per cent) and Peru. B. coli of man can be transmitted to monkeys, cats, guinea pigs, and rats, but the importance of these animals as reservoirs is minor. Handling pigs in slaughterhouses may be an occupational risk.
This ciliate can be a tissue invader, and similar factors to those mentioned for E. histolytica may well determine this behavior. Proteolytic secretions produce necrosis and ulceration of the mucosa. Columns of balantidia may be seen lying in the submucosa. Secondary infection with bacteria results in an accompanying inflammatory reaction. The ulcers are often quite large and deep, with a broad, indurated base. A liver abscess with B. coli in situ has been described, and italantidia have been found in the lung and heart in isolated cases.
Less than one fifth of infected persons have symptoms. Severe infections are associated with diarrhea and the passage of blood and mucus in the stools. Constitutional symptoms of fever, nausea, vomiting, and asthenia are described. Examination of fresh stools reveals the trophozoite or cyst.’ Culture of the stools on media similar to those used for amebiasis may reveal an infection when conventional microscopy has failed; in symptomatic patients this is usually not necessary.
Balantidiasis must be differentiated from amebic dysentery and ulcerative colitis. Although arsenical preparations have been used in the past, oxytetracycline is probably the drug of choice in an adult dose of 500 mg. three times a day for ten days. Paromomycin (Human or metronidazole (Flagyl) is also effective. Spontaneous recovery has been noted. The infection may be fatal if bowel perforation occurs.