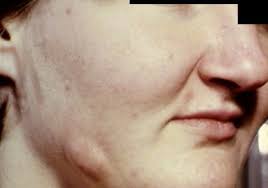
Actinomycosis is a chronic, systemic disease characterized by multiple indurated abscesses and sinus tracts characteristically in the face, neck, chest, and abdomen.
History of Actinomycosis .
Lebert is credited with the first report, in 1857, of actinomycosis in man. Bollinger described the disease in cattle in 1876. In 1877 Harz named the causative organism Actinomyces bovis. In 1878 Israel clearly defined the disease in man by a summary of the clinical and pathologic characteristics observed in 38 patients. The same author in collaboration with Wolff in 1891 succeeded in growing the microorganism in anaerobic culture. In 1910 Lord observed A. bovis in and about carious teeth and tonsillar crypts in the mouths of otherwise normal persons.
Etiology of Actinomycosis .
Actinomycosis in man is caused by A. israelii and in cattle by A. bovis, but species characteristics overlap. In the normal mouth A. israelii grows as a pleomorphic rod-shaped bacterial form and in tissues as a granule. In draining pus, mycelial clumps measuring 1 to 2 mm. in diameter and white to yellow in color have been termed “sulfur” granules. Microscopically these are composed of 0.5 to 1.0 /a hyphae which stain gram-positive. On agar media under strictly anaerobic conditions, A. israelii grows as a white spherical or lobulated colony. Laboratory animals are not, generally, susceptible to experimental infection.
Epidemiology of Actinomycosis .
The disease is worldwide in distribution. During the first part of the twentieth century it was the most common of the systemic mycoses but has been decreasing lately. Males are affected almost twice as frequently as females, and illness seems more common among farmers and in rural areas. Disease is produced by direct invasion of contiguous tissues by A. israelii commonly present in the mouth or bowel. There is usually concurrent infection with anaerobic Disease in the brain, heart valves, or extremities. In tissues the characteristic and classic findings are the actinomycotic granules. These are usually found in abscesses and are surrounded by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Chronic granulomatous reactions are also seen with giant cells, especially about granules.
Clinical Manifestations And Cervicofacial Form.
The cervicofacial form occurs in approximately half of all cases. Infection probably spreads secondarily to trauma or to carious teeth or infected tonsils. The subcutaneous tissues at the angle of the mandible and of the neck have a characteristic “woody” feeling, and the skin over these areas :s reddened and may have single or multiple draining sinus tracts. Pain is seldom prominent even with osteomyelitis or periosteal lesions of bone.
Thoracic Form of Actinomycosis .
In 15 per cent of cases disease arises from aspiration into the bronchi of A. israelii or in a few instances from extension of disease from the esophagus to mediastinal tissues and secondarily to pleura and lung. Fever and cough are minimal early in the illness. As disease progresses to consolidation, pleurisy, and draining sinuses, prominent symptoms are weight loss, night sweats, and high fever. Rib involvement occurs occasionally, pleural effusion rarely.
Abdominal Form in Actinomycosis .
Actinomycosis of the abdomen generally follows appendicitis, appendiceal abscess, a perforating lesion of the stomach, or a diverticulum of the large bowel. An abdominal mass is usually palpable, and may be extensive; and there may be burrowing sinus tracts, some of which may open to the skin in the inguinal or other regions. Retroperitoneal and thoracic spread :through the diaphragm are common.
Other Forms.
Approximately 10 per cent of patients- have lesions in the brain, heart valves, anorectal area, or subcutaneous tissue of the extremities. Rare instances of actinomycosis of the unger have been attributed to injury to the hand by an adversary’s tooth.
Diagnosis of Actinomycosis
The diagnosis of actinomycosis is supported by the finding in pus of granules that are composed of gram-positive, branching, often beaded hyphae. It should be emphasized that granules may be expressed from i cyberwise normal tonsils and may not be found in cerebrospinal fluid in cases of central nervous system disease. The diagnosis is confirmed by the asolatxm of the micro-organism in anaerobic culture from a lesion.
Treatment of Actinomycosis .
Penicillin, first used for actinomycosis in 1944, continues to be the best drug in treating all forms of the disease. Although most strains are inhibited in vitro by levels of 0.1 unit per milliliter, the nature of the pathologic process leads often to treatment failures and necessitates prolonged therapy. Doses of 1 to 20 million units daily for at least six weeks or until lesions have healed are recommended. Other antimicrobial drugs, especially tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and streptomycin, may be of supplemental benefit.Surgical resection and incision and drainage of chronically infected tissues are important adjunctive therapeutic measures.
Prognosis of Actinomycosis .
Prior to antimicrobial therapy, prognosis for life was poor in all forms. With penicillin therapy, the approximate recovery rates are: cervicofacial, 90 percent; and 80 per cent; and thoracic, 40 percent.