If you want to clarify all your doubts, on what a food web examples this article is for you. The energy that living beings need to perform vital functions is obtained through food.
Depending on their diet, living beings can belong to one trophic level or another. These trophic levels constitute the trophic chains, which are nothing more than abstract representations of the energy flows in ecosystems. Sometimes it is difficult to distinguish between the concepts of trophic chain, trophic web and trophic level.
Food Web Examples You Must Know.
Examples of terrestrial food chains
As examples of terrestrial trophic chain we indicate some of those that occur in the Mediterranean forest :
- Broom (primary producer) -> aphids (primary consumer) -> blue tit (secondary consumer) -> imperial eagle (top predator).
- Rosemary (primary producer) -> rabbit (primary consumer) -> lynx (top predator).
- Cork oak (primary producer) -> grasshopper (primary consumer) -> wild boar (secondary consumer) -> lynx (top predator).
Examples of aquatic food chains
In aquatic ecosystems, trophic chains are longer. As examples of an aquatic trophic chain, we indicate some marine trophic chains and some freshwater ones.
Examples of marine food chains
Three of the examples of marine food chains are as follows:
- Green algae (primary producer) -> molluscs (primary consumer) -> Cottus cognatus (secondary consumer) -> king salmon ( tertiary consumer ).
- Phytoplankton (primary producer) -> zooplankton (primary consumer) -> sardines (secondary consumer) -> tuna (top predator).
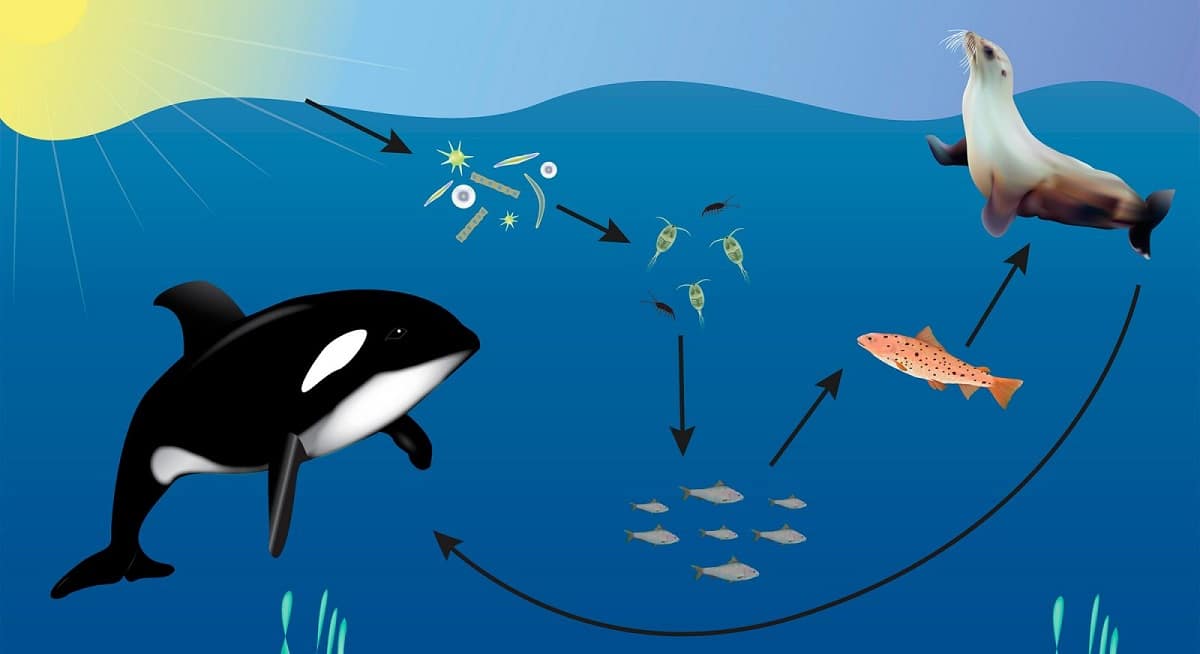
- Diatoms (primary producer) -> krill (primary consumer) -> blue whale (secondary consumer) -> killer whale (top predator).
Examples of freshwater aquatic food chains
Within the examples of freshwater aquatic food chains we can find the following cases.
- Algae (primary producer) -> water fleas (primary consumer) -> catfish (secondary consumer) -> herons (tertiary consumer).
- Aeneas (primary producer) -> grasshopper (primary consumer) -> frog (secondary consumer) -> gray heron (tertiary consumer).
Now that you know the examples of aquatic food chains, let’s see the difference between a food chain and a food web.
Difference Between Food Chain and Food Web
The main difference between a web and a food chain is that the chains are isolated relationships of the food web. That is, the trophic web describes the set of trophic chains present in a given ecosystem.
That is why trophic webs offer a more realistic representation of the feeding relationships that occur in a community. However, such food webs are more complex and difficult to represent and, therefore, it is usually easier to study food chains separately.
Some of the main characteristics of trophic chains are:
- Energy transfer occurs from simple organisms to more complex organisms.
- The arrows indicate the direction of energy transfer (unidirectional).
- The links in the food chain or trophic levels are each represented by a species.
- Keystone species are capable of modifying trophic chains, since their presence/absence controls the abundance of other species due to the position they occupy in the trophic web