Tuberous sclerosis is a congenital disease characterized by the presence of congenital tumors and malformations of the brain, skin, and viscera, and clinically by epilepsy and mental retardation.
Etiology of Tuberous Sclerosis
The disease is both sporadic and heredofamilial and is probably inherited through a single dominant trait.
Tuberous Sclerosis Pathology.
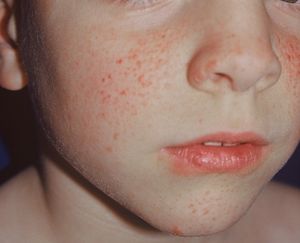
The brain, although usually normal in size, is studded by many small nodules or tubers. These are firm, and occasionally calcified. Sometimes they distort the normal configuration of gyri and may project into the cerebral ventricles, where they present as char- acteristic “candle gutterings.” Microscopically, the tubers are composed of nests of glial fibers and abnormal ganglion cells. They may undergo gliomatous degeneration or develop into meningiomas. Glial tumors of the retina (phakomas) and gliomatous tumors of the nerve head and optic tract are also found in some cases. Adenoma sebaceum, the characteristic skin lesion, is a small firm tubercle often found over the nose and cheeks.
They are rarely present at birth, but usually develop during the first decade toward puberty. Although tending to cluster over the bridge of the nose and the cheeks, they may be found elsewhere over the head. In addition, a variety of other polyps, subcutaneous nodules, pigmented warts, and café-au-lait spots similar to those of von Recklinghausen’s disease are found. Hypopigmented macules may be the earliest cutaneous manifestations. Mesodermal tumors of the kidney, liver, pancreas, lung, and thyroid gland are seen, along with rhabdomyoma of the heart.
Tuberous Sclerosis Clinical Manifestations.
The presenting symptom Of this disease is usually epilepsy, which appears in the first few years of life. The attacks may present as minor or focal seizures, but in time generally progress to major motor convulsions. Mental retardation is usually noticed during the early years of life and may vary in degree, differing in no way from mental retardation from any other cause. Some patients, however, may have normal I.Q.’s. The adenoma sebaceum usually appears toward the end of the second or the beginning of the third year of life as small, lightly pigmented, shiny papules that appear vascular.
They may first appear on the malar areas, but as they proliferate they become confluent and more deeply pigmented, and extend in a butterfly distribution over the nose and cheeks. The retinal lesions are flat, white or gray, round or oval areas, and are present in almost half the patients. Subungual fibromas on the toes or fingers may be seen but most commonly not until after puberty. Patients with mild or partial forms of the disease are not uncommon.
Course and Prognosis of Tuberous Sclerosis
The disease is usually progressive. The outlook in individual cases, however, depends on the severity of the mental impairment and the frequency and intensity of seizures. It must be emphasized that the three cardinal features of the disease may occur singly or in any combination with varying degrees of severity in members of the same family. Often the defects are progressive, and death occurs in the second decade of life. The development of gliomatuus changes in the brain may also shorten the course of the disease, as may progressive pulmonary insufficiency from pulmonary tumors. Sudden death from rhabdomyorna or the heart may occur.
Treatment of Tuberous Sclerosis
The treatment is the same as that for epilepsy with appropriate measures for the mental retardation. Institutionalization is sometimes indicated.